In this article, we will discuss and learn How blockchain is being used in supply chain management. You already understood what is blockchain through carefully reading this article https://infotechabout.com/what-is-blockchain-technology-concepts/ and built your basic foundation on blockchain technology. If you didn’t read this article please read the article first.
Now we are moving towards our key topic of how blockchain is used in supply chain management. Before going to discuss in detail first I will explain how tokenization is being used to transfer physical assets.
Tokenization for transferring Physical Assets
Let’s pick an example of how you can apply blockchain tokenization to a physical asset. For instance, a luxury watch that’s making its way through a supply chain. If I have a luxury watch and I am transferring that luxury watch to someone else, how do you keep track of it on the supply chain?
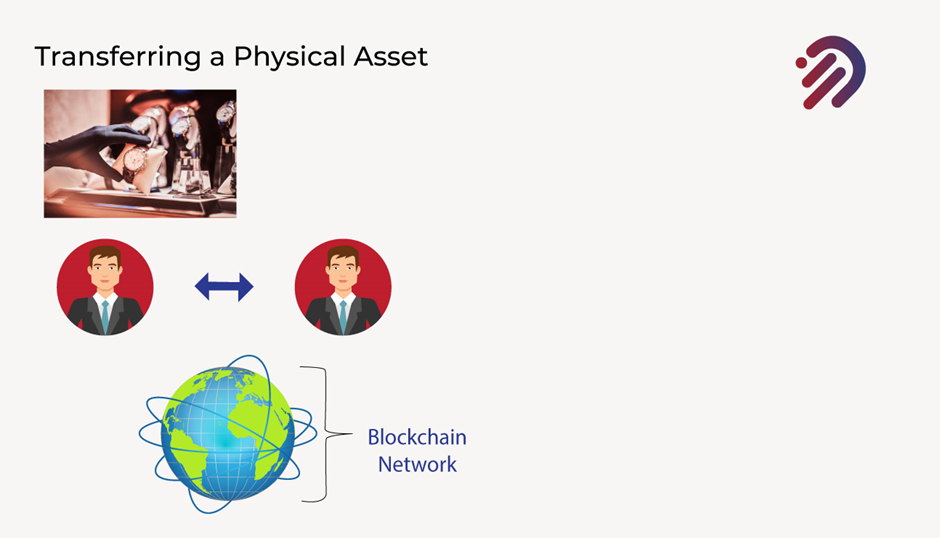
How are you able to transfer and track it on the blockchain?
Well, you can do that through the process of tokenization, which is the process of representing an asset as a token that can be stored, recorded, and transferred on a blockchain. Let’s go back to the example of a luxury watch. If I take that watch and I want to track it as it makes its way through a supply chain, I can basically create a token and represented it as a digital token. And to that digital token, I can assign metadata for the item that made a data will include the history/details of that watch there will be any authenticity certifications that are assigned to that watch Keep track of the history of the manufacturing & steps involved. All that information can be captured and added to that digital token as metadata and you can take that digital token and assign it a unique identifying QR code. And by doing this, you can constantly keep track of where that asset is by following where that QR code is.

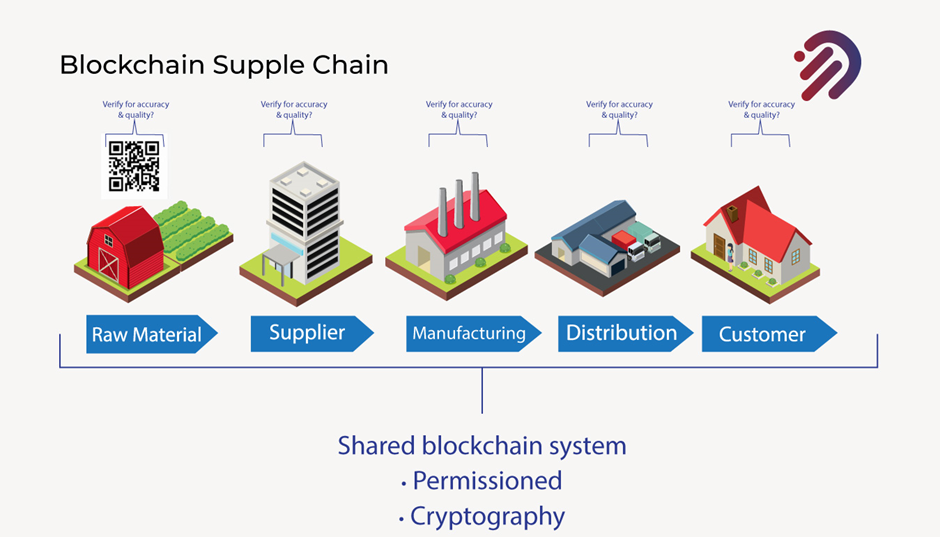
Now, Let’s explain by defining the supply chain as steps involved in getting products from raw materials to the customer.
How to apply Blockchain in Supply Chain Management

This is a very simplistic look of it, but basically, that is what the supply chain is. And it involves all these different steps.
Now let’s begin with the various elements. In context, the suppliers and vendors provide the raw materials to the manufacturers. These manufacturers take the raw materials and transform them into products to sell. Once that’s done, you get to distribution, which is how you get those products out to the market.
Wholesale retail may even be direct online consumers etc. The ultimate goal is eventually to get to the customer that is your supply chain. Now, if we define it as all the steps involved in getting the products from raw material to the customer, you need to understand that supply chain management and supply chains have been around for a very long time.
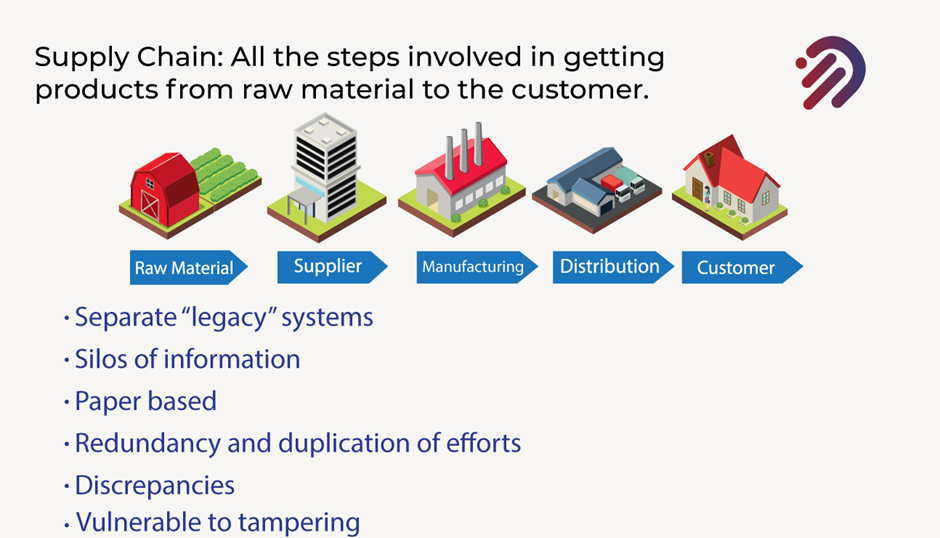
This involves multiple separate legacy systems and this old technology. Some of these have been built for a very long time, and they’re just systems that are in place. They’re working. So right now, as it stands, most supply chains involve separate legacy systems. As a result, you wind up with multiple silos of information that is the raw material. People actually only have their information which is not shared by the suppliers nor the manufacturers and the distributors have only their information. If you’re at the top level, you’re looking at your overall supply chain you have a lot of multiple silos of information kept in separate ledgers and legacy systems. In fact, most of these are paper-based as it currently stands because supply chains have been around for a very long time.
For instance, if you are a farmer and you are delivering Wheat a lot of these are involving paper forms. Because of this, there’s a lot of redundancy and duplication of effort because if you’re filling paper forms you may wind up with multiple steps where people are filling in separate ledgers. As a result, you have redundancy and duplication of efforts all across your supply chain and you will face the issue that there may be discrepancies between these because the way that somebody records the information at one step of the supply chain may not match where it is.
Additionally, this is vulnerable to tampering because if anybody can fill in a paper form or in a legacy system and they can simply include whatever they believe they want to include in that paper form or own format you run into the issue that some people may include incorrect information or perhaps not even provide information. These are all challenges with current supply chains. Now, in a blockchain that is a blockchain-based supply chain and everybody uses a shared blockchain system, the way that you can separate who gets access to what information is by establishing permissions.

What that means is that the raw material people have access to a certain amount of data. The manufacturing people have a completely separate amount of data. The distribution people can have different access to data. However, if you’re at the top level looking at your overall supply chain, you have full access to the entire information and you can see the big picture. In fact, you may be able to open up certain amounts of data across several steps and your supply chain if you believe that it will actually help you provide better efficiencies.
Furthermore, the way that you can do this is by tracking individual assets on your supply chain you create tokens for these different assets actually you assign unique QR codes or various ways to track those unique assets as they make their way through the supply chain.
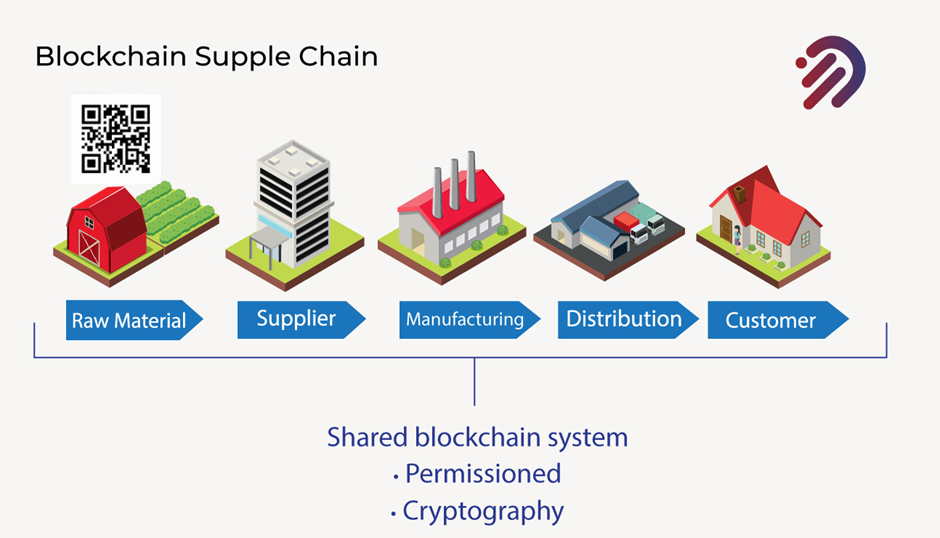
By using cryptography, you’re able to manage who has access to the information and who can determine whether an asset is moving down the supply chain.
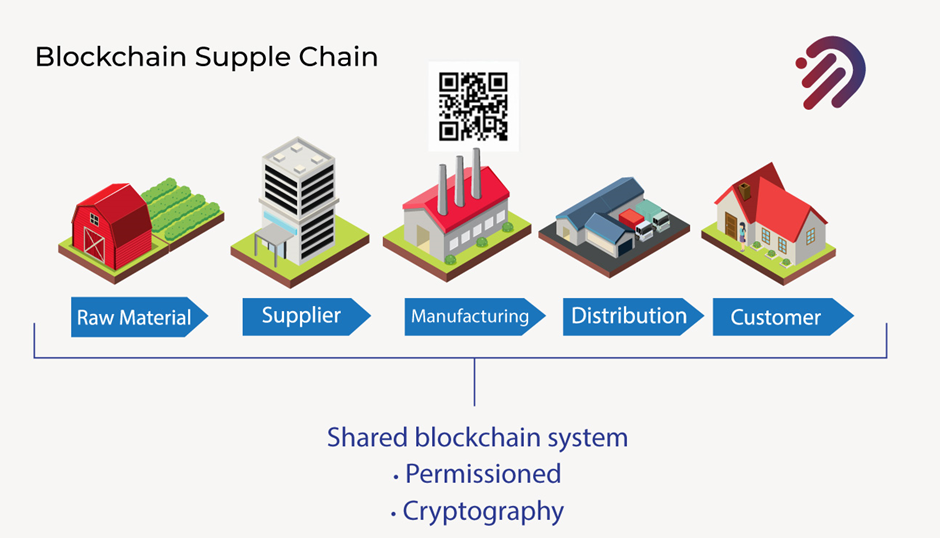
You have full visibility of who can actually sign for the different steps by using cryptography and private keys moving along. You can track the various assets and make their way from raw material to supplier, from supplier to manufacturing, and from manufacturing, to distribution you can track it all the way through to the customer or consumer.
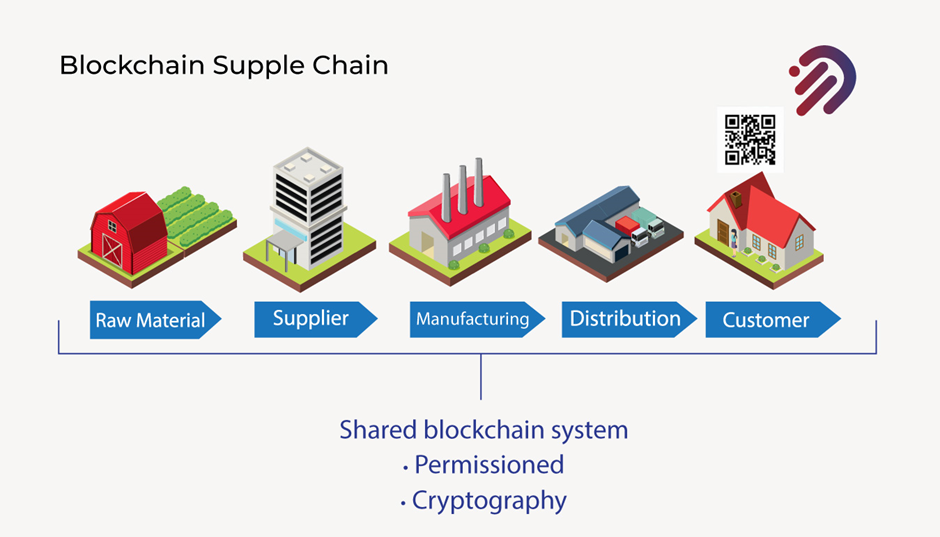
In essence, I am mentioning here a great quote from Paul Brody, who’s the Ernst and young global innovation blockchain leader.
“At its most basic level, the core logic of blockchains means that no piece of inventory can exist in the same place twice.”
Actually, If you think about the supply chain, what you really focus on is that no piece of inventory can exist in the same place twice and you can do that by creating unique tokens for each asset as they make their way through the supply chain.
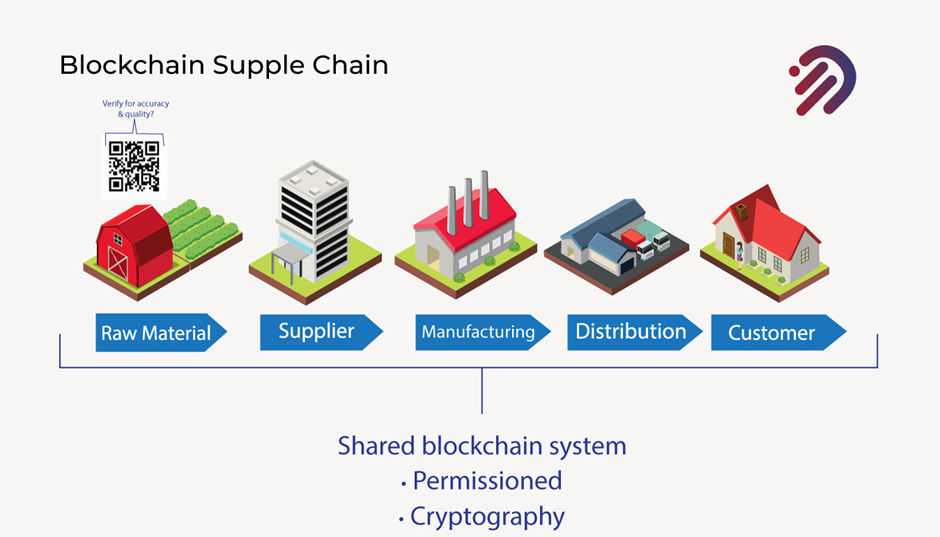
Now there is a challenge. How can you verify the accuracy and quality as it makes it all the way through across all of the steps? In fact, once the asset makes it all the way to the customer? How could the customer have visibility to ensure that all the steps along the supply chain have been properly handled.?
We can handle this through Oracles. Don’t worry it’s not Oracle Database or Company its blockchain’s oracles.
Blockchain Oracles
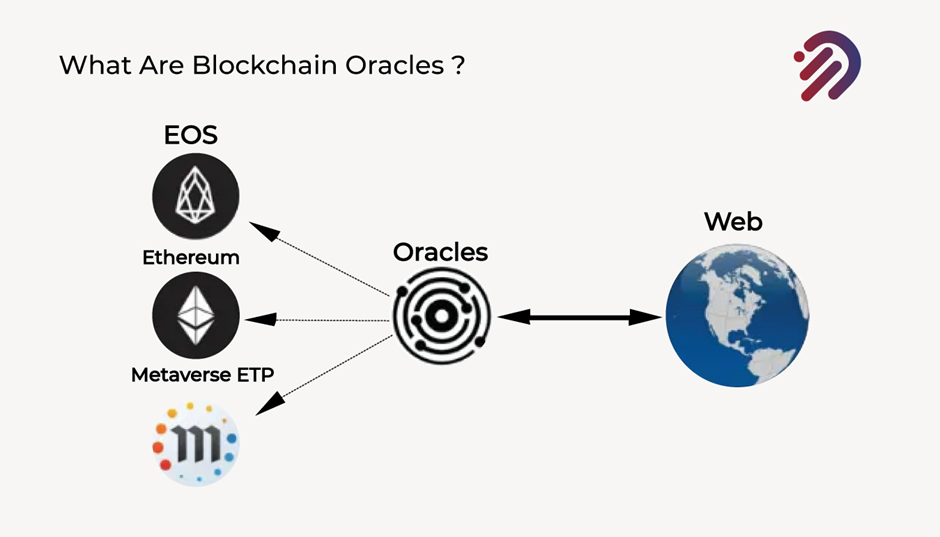
Now we will discuss a key concept in blockchain and supply chain management called blockchain oracles. This concept of oracles is essential when it comes to blockchain and the supply chain because it’s how you verify the accuracy and the quality of the assets as they make their way through the supply chain. Now, in essence, Blockchain oracles are the entities that link the blockchain to other systems, thereby allowing smart contracts to run based on data and inputs from real-world systems. It’s a very loaded or technical statement so don’t worry I am going to explain it here. Let me explain to you a little bit more about that by going over three types of blockchain oracles.
Three Types of Blockchain Oracles
1. Hardware
Oracles can be triggered by a sensor this involves RFID and the Internet of Things (IoT), sensors, barcode scanners, etc. For instance, what you see here are visuals of actual blockchain oracles being used. What you have is a tagged fish on the left that’s actually tagged using an individual unique QR code so you can keep track of that fish as it makes its way through the supply chain. You can tag, for example, beef so individual cows, for instance, or once products make it to different storage places, you can track where they are along the supply chain.

2. Software
The second Level is Software as oracle uses information that’s available online. For example, market data or data triggers.
3. Human
The third level is Human as this could include various inspectors and these are people that verify and research events. They may be quality control people, maybe people at warehouses.
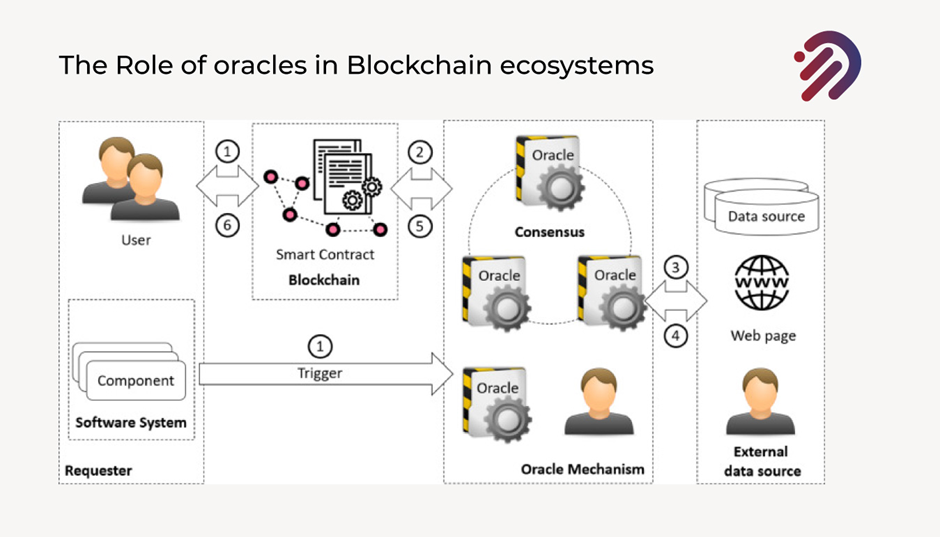
Now, the key thing about these blockchain oracles is that at every step of this supply chain, they are used to verify the accuracy and the quality so that once the product makes it all the way to the customer, you can even provide the customer an option to have their own unique QR code to be able to see the entire provenance (original) of a product as it made its way through the supply chain and I will be presenting some examples of this as we move forward in this article.
There are a few challenges you need to know about oracles.
Challenges with Oracles:
- Oracles are third parties that need to be trusted
- It is critical that the source of the information is trustworthy (If you’re actually using a human to verify a specific step of the blockchain. if that person records incorrect information, that information will be recorded permanently and immutable, even though it is wrong. So it’s very important that you actually can trust the source of this information)
- Sometimes more than one oracle may be needed to trigger an action
- Using only one source of information may be unreliable (Because you may have outages, somebody may tamper with that one source of information. So often in many blockchain-based solutions, more than one oracle is used at various steps to ensure that the various oracles support each other to provide the most quality and trustworthy information.)
Benefits and Limitations of Blockchain Technology
Now we will talk about the benefits and limitations of blockchain technology. In this section, I will explain specifically to give you the big picture about blockchain, because often you will read about the good things about blockchain, but you don’t hear about the limitations involved so that you see the entire scope as you make your decisions around blockchain technology.
Benefits of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management:
We will now move towards the benefits of blockchain and supply chain management, and to do so, I’d like to tell you about 10 benefits of using blockchain in the supply chain this is not a final list, but it will get into some key areas that you should be aware of when you apply blockchain in your supply chain.
10 Benefits of Using Blockchain in the Supply Chain
- Immutable System of Proof protected by Cryptography & timestamps (you can know exactly when each step is achieved)
- Reduced paperwork and redundancy of data input (Because everybody’s working with the same system instead of actually filling out paper forms they’re using the same computer system)
- Increased Transparency across the entire supply chain (Definitely increased Transparency across all levels of the supply chain)
- The immutable nature incentivizes suppliers to input more accurate data (If you know for a fact that the information that you’re inputting is associated with your private key then you ensure that that information is accurate. Otherwise, when somebody looks at the reports, they can know exactly who input the incorrect information)
- Increase level of Trust in partners (Because partners are more incentivized to actually input correct information)
- Verifiable chain of custody to detect and uncover any gaps
- Full unbroken provenance of assets throughout the supply chain
- Connectivity of IoT devices with data shared across the entire network (For instance, a farmer may include multiple devices that are Internet of Things connected to the supply chain to provide information such as What is the humidity levels? What is the temperature? All that information can be captured and provided and shared across the entire network.)
- Permanent historic record of data of all assets (This can be very valuable over time)
- Smart contracts for instant payments (Which enables you to provide things such as instant payments. This can make the whole process a lot more efficient, and suppliers will be a lot more willing to work with you if you can enable instant payments when they actually are able to provide services. There are many things you can do with smart contracts and automating all things by using blockchain)
Possibilities with Supply Chain on Blockchain:
- Unique Identities for individual items (For instance, a luxury watch can have a unique identity, so you can actually once you actually deliver it to the customer. The customer can track that unique identifier and see the entire history for that one unique item)
- Cryptographic, verifiable seals for authentic products (Products by having a cryptographic, verifiable seal for exclusively authentic products. You can make sure that every single product that’s produced is authentic)
- Tracking responsibly sourced products all the way through consumers (For consumers that are very focused on sustainably sourced products, you can actually provide them that information by giving them the entire provenance of the product, including the actual providers and the suppliers. For every step along the way)
- On-Demand manufacturing can reduce fakes by controlling the number of units made (Because you know exactly how many units of a specific product are being created, and you can keep all that information tracked on the blockchain. You can create on-demand manufacturing. So instead of creating surplus amounts of a product, you only create what is required. This is also possible by capturing all that information on a blockchain)
- New digital experience around products (This can be possible and explore that other than currencies many digital products were introduced through blockchain)
Limitations of Blockchain:
As you evaluate whether to use blockchain or not in your supply chain, I want you to be aware of some limitations of blockchain. It’s important to know that there are many benefits to using blockchain, but there are some key limitations as well, and you need to understand these as you actually consider whether to use blockchain or not.
Limitations of Blockchain Technology:
- It is Immutable (Which means there are no reversals, modifications, or deletions)
- No Reversals or Modifications (If you have a business process where you usually do modifications to certain orders the only way that you can actually modify records on a blockchain is by creating a new transaction that makes a modification and you do not eliminate the original one. You will always keep a copy of the original transaction and you will only append a new block of transactions and include a new transaction that changes what the results of the first one were and this is not true modification, what you are doing is creating a new transaction that may affect the results that were recorded previously and sometimes we do in legacy on our financial ledger that freeze or locked.)
- Key Management (It is essential when it comes to the blockchain as I earlier discussed blockchain uses cryptography and the concept of private keys is very important in blockchain as that is how you can keep track of who has performed what within the blockchain. As a result, these private keys are critical to the safety and integrity of the blockchain and you need to be very certain that the way you manage those keys is as secure and as tight as possible)
- Scalability (Blockchain keeps track of every single transaction done. As a result, you manage very large data sets. This may present some challenges to people who have very large numbers of transactions. The things you need to consider are as you increase the size of the network and add additional nodes. There may be challenges involved as you scale that blockchain out. As I earlier shared the size of the bitcoin blockchain is increasing day by day)
- Time to Process (What I mean by this is that while it is very, very fast to have a centralized database where you can just make a change and the changes are reflected instantly when you’re dealing with blockchain, you have multiple copies of the blockchain and you need to wait until you actually achieve consensus across all the nodes that have a copy of that blockchain. As a result, the time to process can be far slower than actually a centralized database solution)
I hope you have covered everything about Blockchain and how to Blockchain in supply chain management and you have sound knowledge of blockchain technology in the supply chain, however, if you have any queries feel free to comment or contact me through email yousuf@infotechabout.com.
in the upcoming article, I will try to cover some practice through blockchain technology demonstration or will also cover a demo for blockchain in supply chain management.






